Roman
Ancient Rome was a civilization that grew out of a small agricultural community founded on the Italian Peninsula as early as the 10th century BC. Located along the Mediterranean Sea, it became one of the largest empires in the ancient world.
In its centuries of existence, Roman civilization shifted from a monarchy to an oligarchic republic to an increasingly autocratic empire. It came to dominate South-Western Europe, South-Eastern Europe/Balkans and the Mediterranean region through conquest and assimilation.
Plagued by internal instability and attacked by various migrating peoples, the western part of the empire, including Italy, Hispania, Gaul, Britannia and Africa broke up into independent kingdoms in the 5th century AD.
The Eastern Roman Empire, which was governed from Constantinople, comprising Greece, the Balkans, Asia Minor, Syria and Egypt, survived this crisis. Despite the later loss of Syria and Egypt to the Arab Islamic Empire, the Eastern Roman Empire would live on for another millennium, until its last remains were finally annexed by the emerging Turkish Ottoman Empire. This eastern, Christian, medieval stage of the Empire is usually referred to as the Byzantine Empire by historians.
In its centuries of existence, Roman civilization shifted from a monarchy to an oligarchic republic to an increasingly autocratic empire. It came to dominate South-Western Europe, South-Eastern Europe/Balkans and the Mediterranean region through conquest and assimilation.
Plagued by internal instability and attacked by various migrating peoples, the western part of the empire, including Italy, Hispania, Gaul, Britannia and Africa broke up into independent kingdoms in the 5th century AD.
The Eastern Roman Empire, which was governed from Constantinople, comprising Greece, the Balkans, Asia Minor, Syria and Egypt, survived this crisis. Despite the later loss of Syria and Egypt to the Arab Islamic Empire, the Eastern Roman Empire would live on for another millennium, until its last remains were finally annexed by the emerging Turkish Ottoman Empire. This eastern, Christian, medieval stage of the Empire is usually referred to as the Byzantine Empire by historians.
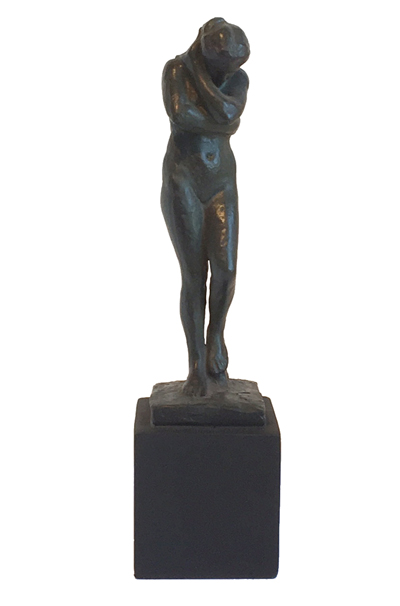

Eve by Rodin - Polyresin
$31.76
![]()
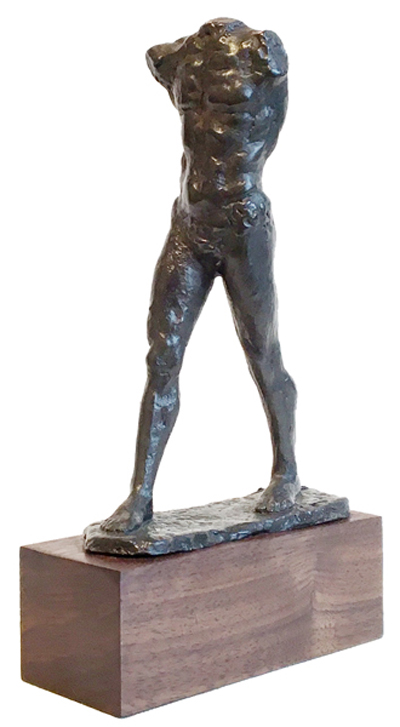
Walking Man by Rodin - Bronze
$395.00

Assyrian Star Mask
$11.00

Edgar Degas "Arabesque Ballerina" Bronze
$1,368.75

Lamassu Magnet, Set of 4
$17.52

Lamassu Freestanding - Bronze
$5,256.00